Science & Research
The most unique ability of ImmuOligo is to help animals balance its own immune response, a process called the biological response modification (BRM). BRM is critical to the overall health of the animal. It is important to understand that the animal’s immune system can either down-regulate or up-regulate depending on different types of physical and environmental factors in order to protect itself.
It is therefore a common misconception that one always needs to boost the immune system, especially during circumstances of seasonal stresses when the immune response simply needs to down-regulate rather than being boosted. In fact, too much of a boost can even make the animal feeling worse than it did to begin with.
Research has shown ImmuOligo has a distinct advantage to promote a robust and balanced immune response which is crucial to having a healthy productive animal.
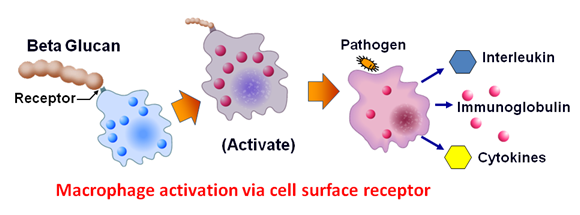
ImmuOligo exerts its beneficial effect through multiple pharmacodynamics. The induction of cellular responses by ImmuOligo involve their specific interactions with several cell surface receptors such as complement receptor 3 (CR3; CD11b/CD18), dectin-1, lactosylceramide, and selected scavenger receptors. Classified as biological response modifiers, ImmuOligo demonstrated enhanced microbial defensive mechanisms by activating monocytes and neutrophils in both in vitro studies and target animals after ImmuOligo administration. As a consequence, both innate and adaptive immune response can be primed by ImmuOligo.
ImmuOligo also serves as prebiotics that promotes specific changes in the composition and/or activity of the gastrointestinal microbiota which, in turn, confers benefits on host well-being and health.
Scientifically proven, high purity isolates make ImmuOligo superior than other commercial available products
Patented manufacturing processes preserves active isolates for performances
Simple & reliable quantification analysis to verify active isolates: beta 1,3/1,6-glucan contents
Never boost-A balanced immune system is the key to health & performance
We adhere to a philosophy of quantitative integrity, whereby a product must not only be supported by sound theory, but must also be grounded in evidence-based research
Studies and Trials
Engineered to deliver performance, the R&D of ImmuOligo has always been an ongoing process which effectively demonstrate that the ingredient safely supports animal health, helps increase species-specific performance, and promotes wellness under stresses.

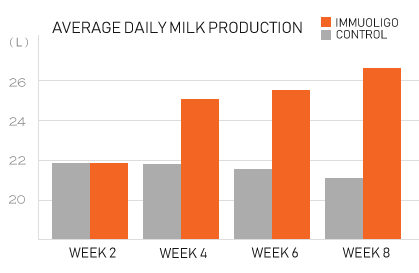
Shown to increase average daily milk production
A recent university study with healthy Holstein cows using ImmuOligo Dry for a consecutive period of 56 days to investigate on milk production, milk quality, and general health. Results show a statistically significant (p<.05) difference in average daily milk production between the control and intervention group taking ImmuOligo as part of the daily supplement program.

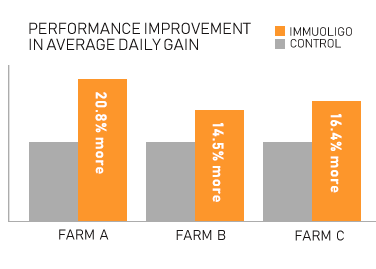
Shown to promote healthy and continuous growth among neonatal calves
A recent trial with neonatal dairy calves using ImmuOligo for a consecutive 28-days. The result demonstrated that there is a statistically significant difference in percentage improvement in Average Daily Gain ranging from 14.50% to 20.80% among ImmuOligo group as compared to the control (p<.05).

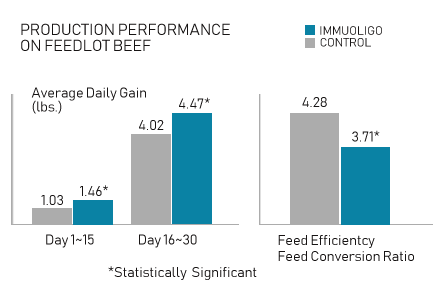
Improve feed efficiency by increasing gains (ADG) & optimizing feed efficiency
Results from a field trial with feedlot beef cattle using ImmuOligo for a consecutive period of 30-day feeding period show statistically significant improvements in average daily gain (ADG) and feed conversion rate (FCR) as compared to the control group (p<.05).

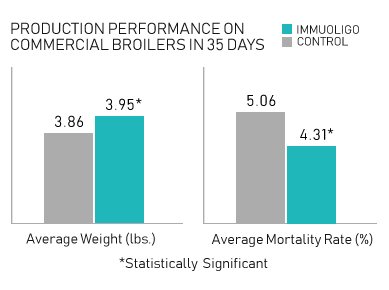
Maximize performance in commercial poultry production
A pending-published study taken place in a CA-based poultry facility shows feeding ImmuOligo for a consecutive 35-days resulted in a statistically significant improvement in average body weight and mortality rate in the intervention group versus control (p<.05).

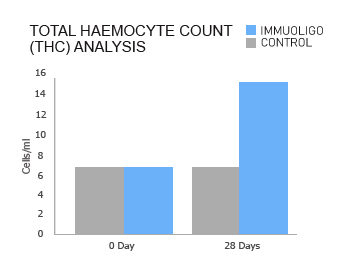
Strengthens innate defense for commercial shrimp production
In a published study (Chen et al, 2014), pacific white shrimps (L. vannamei) fed ImmuOligo for consecutive 28-day period exhibited a statistically significant higher Total Haemocyte Count (THC) than control. An upgraded haemolymph THC, indicates there is an increased number of immune cells to adapt to environmental challenges and increase prospective yield from a commercial shrimp production operation.